Plant-based diets have gained significant attention in recent years, especially regarding their potential health benefits. At their core, these diets emphasize an abundance of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and seeds. They often limit or exclude animal products, which can lead to a variety of health improvements, including weight management and enhanced energy levels. Many people are curious about the connection between diabetes and plant-based diet, as research suggests that this type of eating may help reduce the risk of developing diabetes.
One of the key aspects of a plant-based diet is its rich nutrient profile. Foods such as leafy greens, berries, and legumes are packed with vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Fiber, in particular, is essential for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. It slows down the absorption of sugar, preventing spikes in glucose that can be harmful to those at risk for diabetes. By incorporating high-fiber foods into their meals, individuals can support better blood sugar control and overall metabolic health.
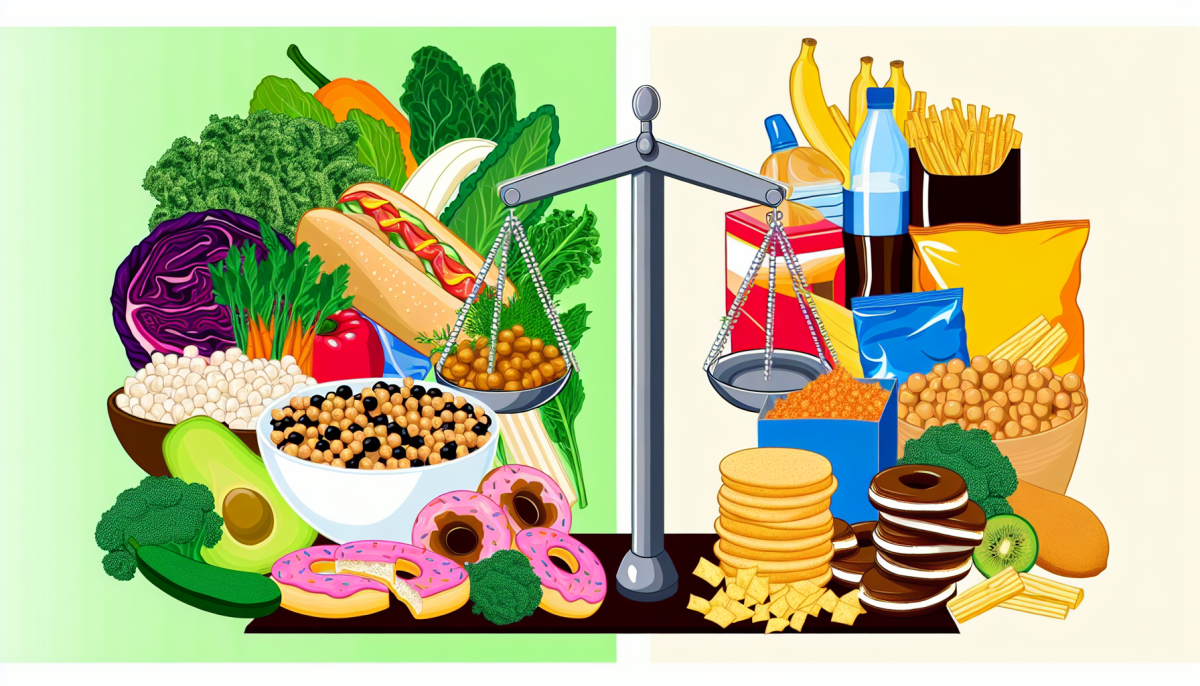
Moreover, studies indicate that those who follow a plant-based diet tend to have lower body weight and body mass index (BMI). Excess body weight is a significant risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes, so maintaining a healthy weight is vital. The emphasis on whole, unprocessed foods in a plant-based diet can lead to a reduction in calorie intake, making it easier to achieve and sustain a healthy weight. As the connection between diabetes and plant-based diet continues to emerge, many people find themselves exploring this lifestyle as a way to improve their health.
Transitioning to a plant-based diet can also introduce a diverse range of flavors and cooking techniques. This not only makes meals more enjoyable but also encourages individuals to experiment with new ingredients, such as quinoa, chia seeds, and various types of beans. By broadening their culinary horizons, people can create delicious, satisfying dishes that promote both pleasure and wellness. Overall, the link between diabetes and plant-based diet highlights a promising approach to health that many individuals are eager to explore.
Benefits for Blood Sugar Control
One of the most significant benefits of a plant-based diet is its positive impact on blood sugar control. Research indicates that diets rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes can help maintain stable blood sugar levels. These foods are high in fiber, which slows down the digestion and absorption of sugars in the bloodstream, preventing spikes that can lead to complications like diabetes and other health problems.
A plant-based diet is also lower in saturated fats and refined sugars, which are often found in animal products and processed foods. By reducing these unhealthy fats and sugars, individuals can decrease their risk of insulin resistance—a major factor in the development of type 2 diabetes. This improved insulin sensitivity means that the body can use sugar more effectively, helping to keep blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
Furthermore, the variety of nutrients found in plant-based foods can enhance overall metabolic health. Foods like nuts, seeds, and leafy greens are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that help regulate glucose levels in the body. By incorporating these nutrient-dense foods into daily meals, individuals not only support blood sugar control but also invest in their long-term health, potentially warding off diabetes and other chronic diseases.
Key Foods to Include
Leafy Greens: Start with dark leafy greens such as spinach, kale, and collard greens. These vegetables are low in calories and carbohydrates, making them an excellent choice for those looking to prevent diabetes. They are also rich in antioxidants and nutrients that support overall health. Adding a salad or sautéed greens to your meals can give your body the boost it needs.
Whole Grains: Instead of refined grains, opt for whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and barley. These grains are packed with fiber, which helps slow the absorption of sugar in the bloodstream. Incorporating whole grains into your diet can aid in better blood sugar control and keep you feeling full longer, reducing the chances of overeating.
Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are staples in a plant-based diet and are incredibly beneficial for preventing diabetes. High in protein and fiber, legumes can help stabilize blood sugar levels and provide essential nutrients like iron and folate. Try adding them to soups, salads, or as a base for your meals to make them more filling and nutritious.
Fruits: Fruits are an important part of a healthy diet, even if you're focusing on a diabetes and plant based diet. Berries, apples, and citrus fruits are lower in sugar compared to other types of fruit and are also rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Enjoy these fruits as snacks or blended into smoothies for a refreshing and healthy treat.
Tips for Easy Meal Planning
Planning meals can sometimes feel overwhelming, but with a few simple tips, it can become a breeze, especially when focusing on a diabetes and plant based diet. To start, consider creating a weekly menu. Set aside some time each week to decide what meals you want to prepare. This not only helps to stay organized but also reduces the stress of last-minute cooking decisions that can lead to unhealthy choices.
Embrace batch cooking! Preparing larger quantities of meals that can be easily reheated throughout the week saves time and ensures you always have nutritious options on hand. Dishes like soups, stews, or casseroles are perfect for batch cooking and can be made with a variety of vegetables, legumes, and whole grains—key components of a diabetes and plant based diet.
Make shopping a breeze by creating a grocery list based on your meal plan. Stick to the perimeter of the store where fresh produce, grains, and legumes are typically located. Avoiding processed foods will help you maintain focus on healthy choices that support your goal of preventing diabetes through your plant based meals.
Lastly, keep it simple! Choose recipes that require minimal ingredients and preparation time. Quick, easy meals requiring just a few fresh ingredients can make sticking to a diabetes and plant based diet much more manageable. Focus on whole foods like fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and whole grains that not only nourish your body but also keep your meal planning straightforward.